The Rise of Technology in Health Innovation
Next week in New York City, a select group of 50 innovators from all over the health-tech industry are gathering in recognition of Medical, Media, and Marketing’s (MM&M) Top 40 Healthcare Transformers and Top 10 Innovation Catalysts. These inductees represent the media brand’s honor roll of visionaries, gurus, self-starters, operators, and wonks bravely working to bring about change in the healthcare industry.
As leaders in the movement of healthcare transformation and innovation, these innovators are working every day to identify new or improved health systems, products, and services that improve people’s health and wellbeing. According to the WHO, health innovation “responds to unmet public health needs by creating new ways of thinking and working with a focus on the needs of vulnerable populations. It aims to add value in the form of improved efficiency, effectiveness, quality, sustainability, safety and/or affordability.”
In recent years, healthcare has begun to fully embrace technology as a partner for mutual advancement. This shift has resulted in marked improvements in healthcare - both in the patient experience as well as for providers.
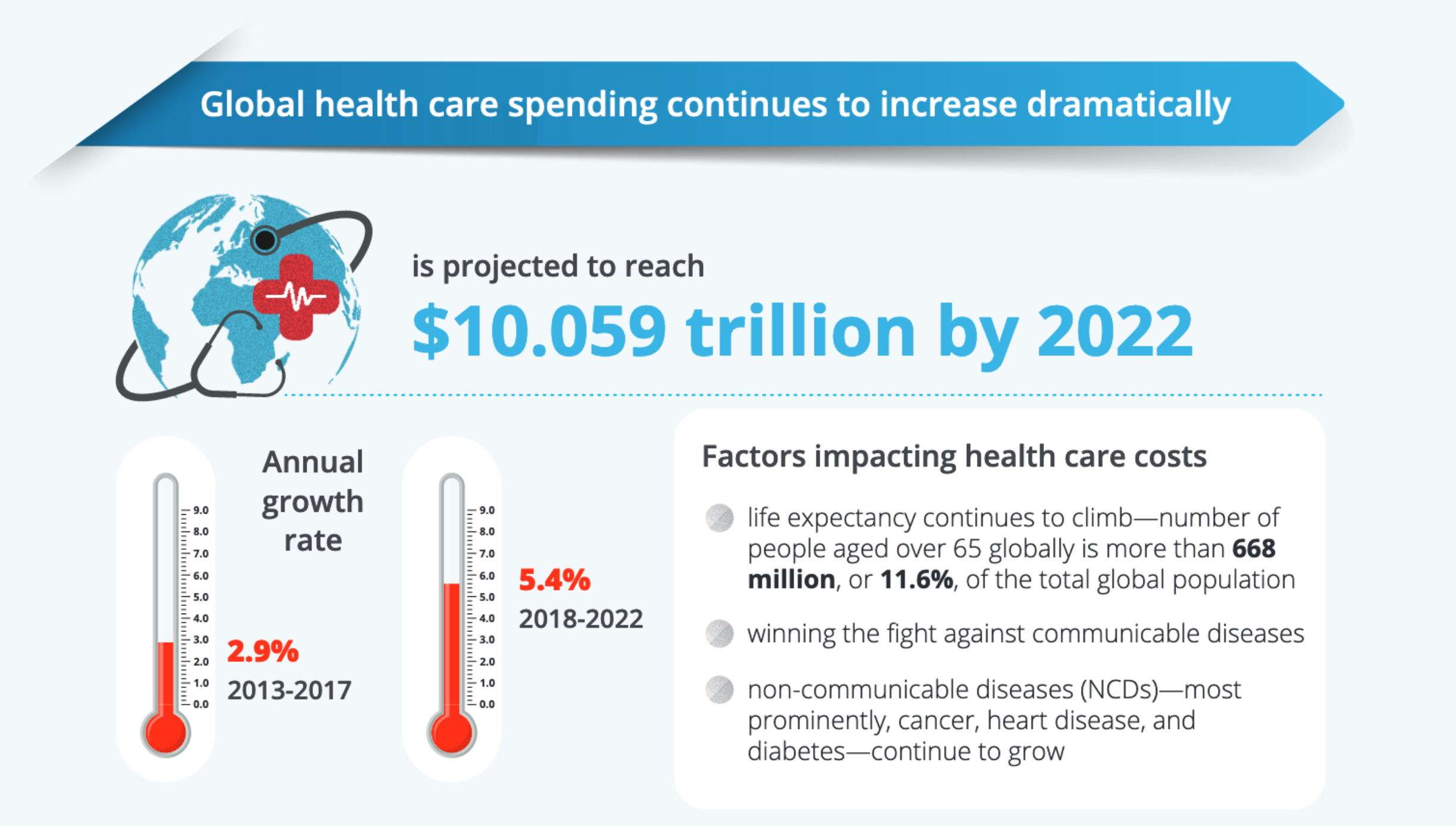
A 2018 Deloitte report on the Global Health Care Outlook projected an increased life expectancy resulting in 11.5% of the population being over the age of 65. Chronic disease rates are also expected to increase, with 642 million people expected to have diabetes by 2040. This aging population coupled with the rise of chronic illness results in an estimated $8.7 trillion in global healthcare spending by 2020.
2018 Deloitte Global Health Care Outlook Report
The role that technology plays in addressing many of these issues facing healthcare cannot be overlooked. A recent roundup by OMERS Ventures outlines a few of the significant innovations that technology has fueled, including:
Empowering the patient: The industry has shifted to a more patient-centric approach where individuals are gaining more control over their own health data, in hopes of ultimately moving towards personalized health care.
Centralizing data: As wearables have resulted in large amounts of health data across multiple devices, the industry is moving to make the information (including all health records) more integrated, actionable and able to flow to clinicians and other care providers.
Increasing accessibility/reducing costs: Technology has enabled the adoption of location-agnostic care, resulting in the emergence of telemedicine and home-based care solutions.
Initiatives like mobile health allow providers to provide high-quality services, and provide patients with cheaper and more accessible care options. According to a report from the American Institute of Medical Sciences and Education, healthcare apps are one of the fastest-growing markets in mobile application development, with 300 thousand apps being downloaded daily.
It should also be noted that while areas of health technology continue to advance, concerns around personal data privacy remain prevalent. Privacy is an especially important need in healthcare, when patients are searching for sensitive condition-related information as well as sharing personal and intimate stories with their peers online. A recent study from the Public Library of Science examined the privacy attitudes among early adopters of emerging health technologies, and found that although these early adopters were willing to share their personal data, they still expressed concerns around who has access to their data and for what purpose. They also shared uncertainties around the privacy implications of their decisions to use new technologies.
Fortunately, there are already companies working quickly to address patient concerns surrounding privacy. Unlike in traditional social media and mobile sites, Curatio users own their own data and are provided with a safe space to share and discuss their conditions in a privacy and regulatory compliant environment.
Researchers have also been exploring the effects of health-tech innovations on population health. In a 2018 study examining the effects of technology on global health literacy, it was demonstrated that social technology in particular will have a growing role in sharing health information. Shared experiences and rapid communication with peers have led to improved health outcomes for patients, particularly in areas where healthcare is less accessible. This type of immediate access to peer support and health education is invaluable to not only manage illness once it occurs, but also to encourage disease prevention and general wellness in all patient populations.
Providing healthcare access to patients using technology is by no means a novel idea, but the companies recognized by MM&M are striving towards even greater innovative and visionary ideas that the industry needs in order to continue pushing the boundaries of growth.